โปรแกรมออกแบบแผงวงจร (PCB Design Tool)
โปรแกรมออกแบบแผงวงจร (PCB Design Tool)
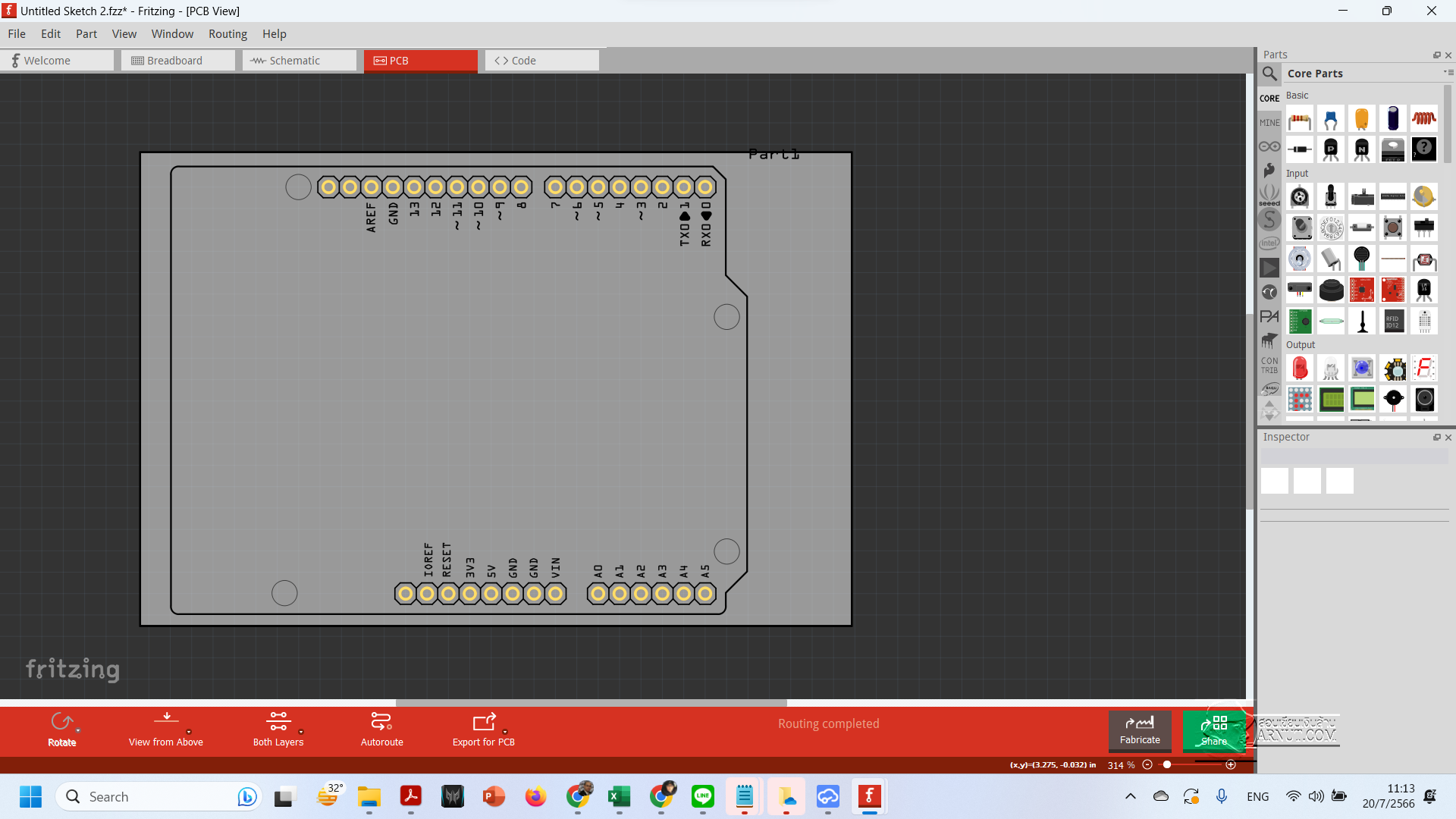
– Fritzing (https://fritzing.org)
Fritzing is an open-source hardware initiative that makes electronics accessible as a creative material for anyone. We offer a software tool, a community website and services in the spirit of Processing and Arduino, fostering a creative ecosystem that allows users to document their prototypes, share them with others, teach electronics in a classroom, and layout and manufacture professional PCBs.
– EasyEDA (https://easyeda.com)
EasyEDA is a web-based EDA tool suite that enables hardware engineers to design, simulate, share – publicly and privately – and discuss schematics, simulations and printed circuit boards. Other features include the creation of a bill of materials, Gerber files and pick and place files and documentary outputs in PDF, PNG and SVG formats.
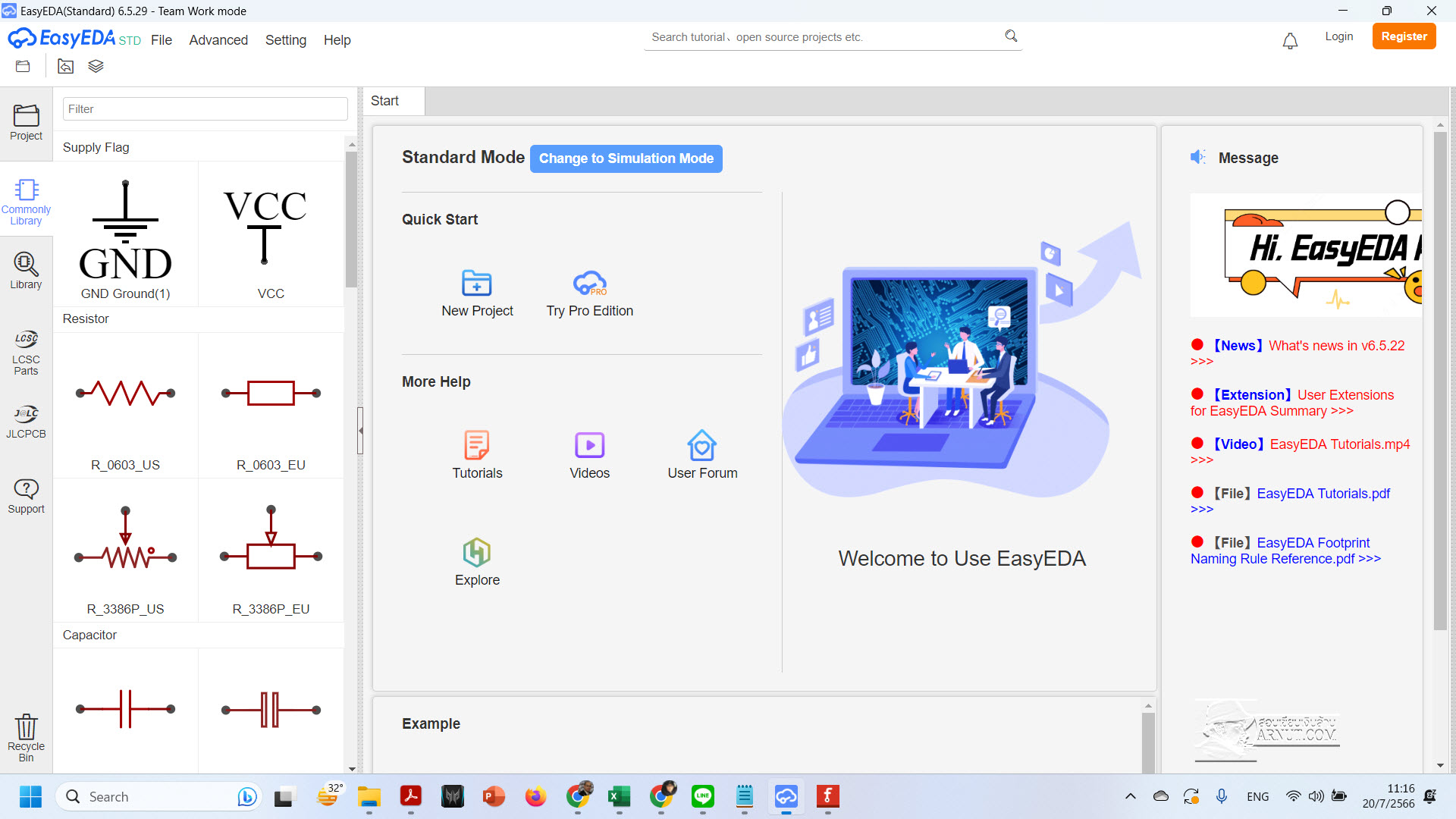
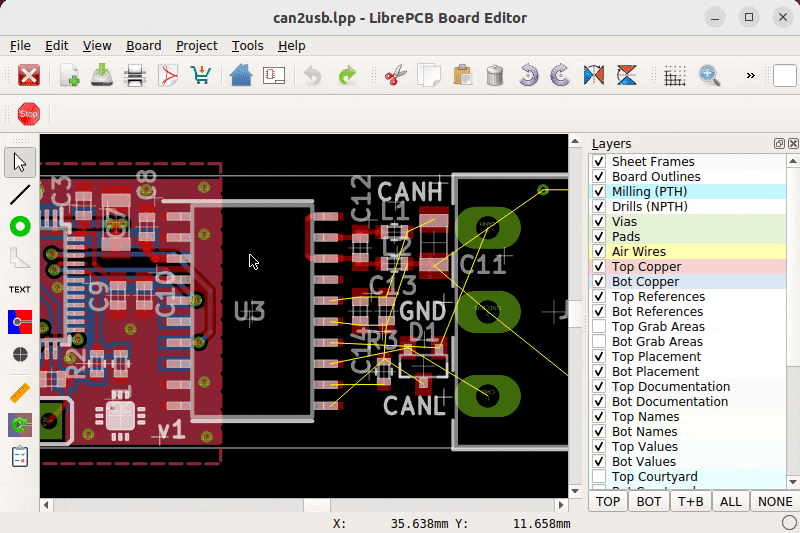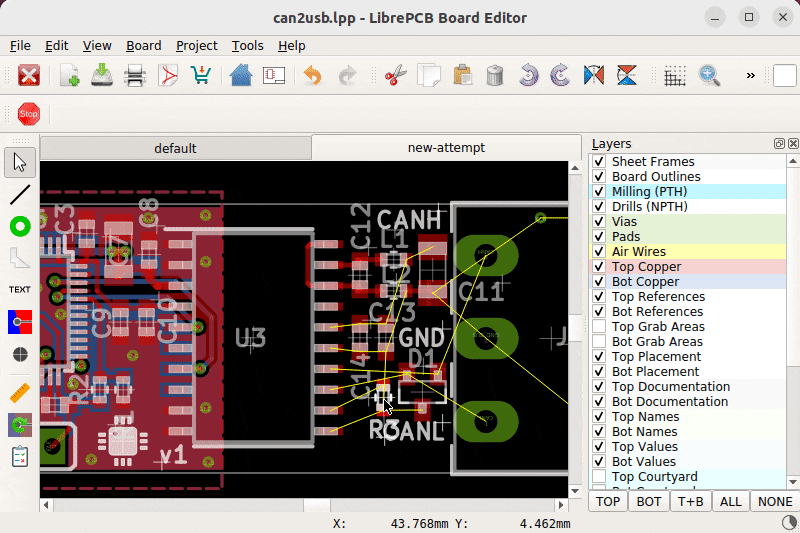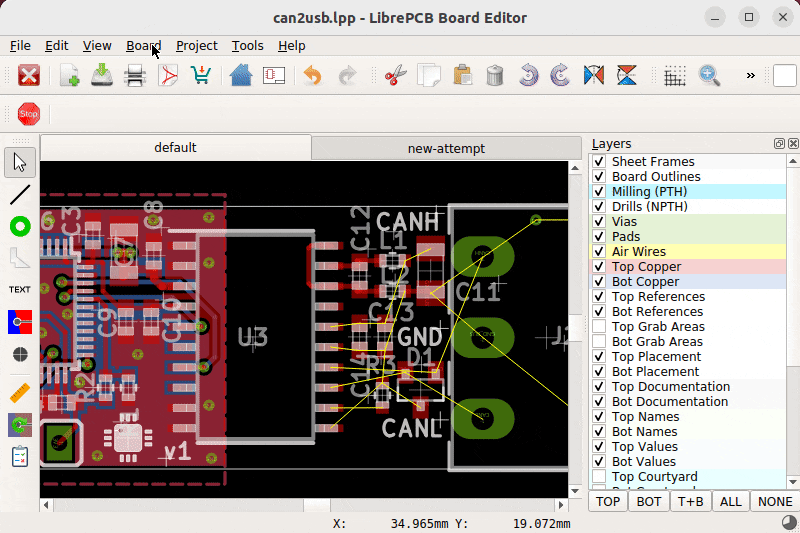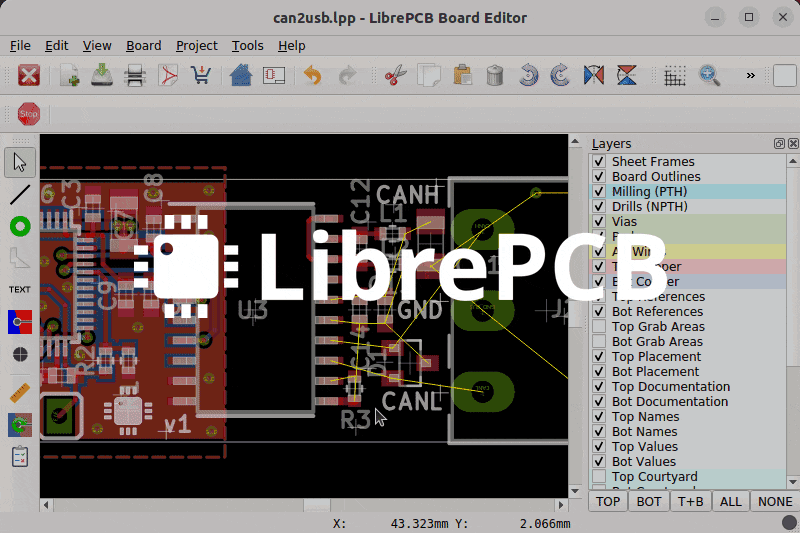
– LibrePCB (https://librepcb.org/features/board-editor/)
LibrePCB is one of the better-known tools belonging to the “new generation” of free PCB design packages. Most older tools have their roots in an age when computers were less powerful, and the choice of components was limited or slower-moving. If those tools were redesigned from scratch, they may look like LibrePCB, which is aimed at a wide range of user experiences. At the same time, all are keen to take advantage of a vast and rapidly evolving spectrum of electronic components, modules, and sensors.
– KiCad (https://kicad.org)
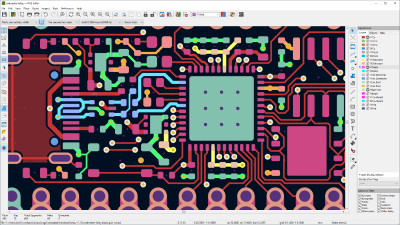
KiCad is one of the most well-known free electronics and PCB design programs. First created almost 30 years ago, it’s now on version 6 and has been extensively upgraded over the last year with significant UI and editor improvements, new design management utilities, and better support for plug-ins. Backed by prominent organizations like the Raspberry Pi Foundation, Arduino, and CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), KiCad enjoys an active community and hosts a well-attended annual conference.
The open-source program boasts a powerful suite of features, meeting the needs of beginners and experts alike. In addition to the usual circuit schematic design, PCB layout tools, and 3D visualization, KiCad integrates circuit simulation (Ngspice), supports Git for version control, and links with FreeCAD for other generic 3D designs. In addition, a growing list of plug-ins provides extension opportunities ranging from RF design to PCB art using Python.
– Upverter (https://upverter.com)
Upverter is an electronic circuit design system delivered in a web browser, which enables hardware engineers to design, share, and review schematics and printed circuit boards. It additionally features the ability to generate a bill of materials, Gerber files, and a 3D rendering. Upverter provides web-based tools for editing schematic diagrams and for laying out printed-circuit boards. It does not require payment for open-source projects.

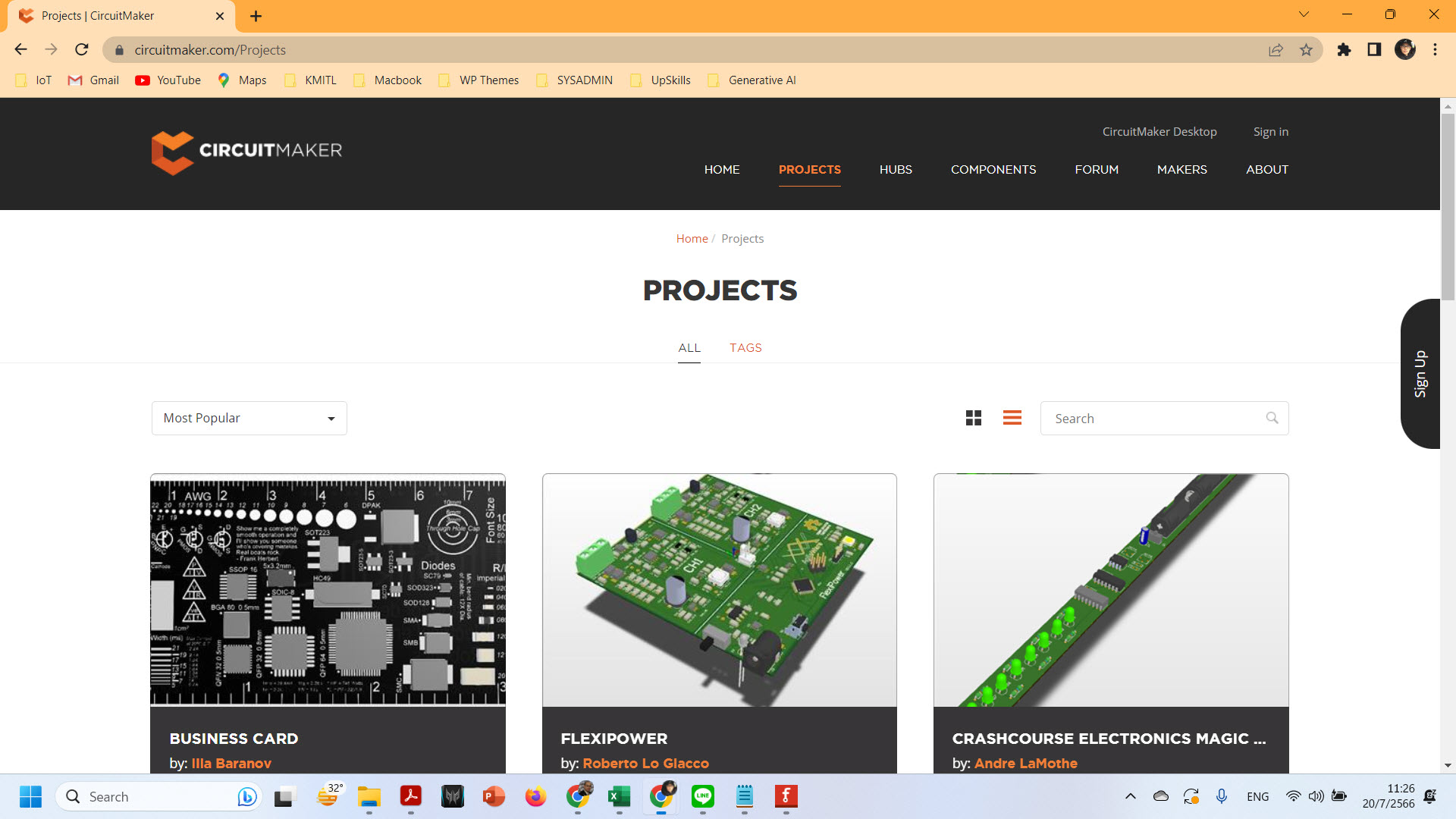
– CircuitMaker (https://circuitmaker.com/Projects)
CircuitMaker is electronic design automation software for printed circuit board designs targeted at the hobby, hacker, and maker community.[1][2] CircuitMaker is available as freeware, and the hardware designed with it may be used for commercial and non-commercial purposes without limitations.
– Osmond (https://www.osmondpcb.com)
Osmond is a little different from the others on this list. Growing out of a personal project by engineer J. C. Chavez, it’s primarily a PCB layout tool that can use circuit netlists generated by other software. It only runs on Mac computers and inherits many user interfaces and usability queues from that platform.
– DesignSpark (https://www.rs-online.com/designspark/pcb-software)
DesignSpark, from the venerable supplier RS Components, is part of an integrated suite of electronic and hardware design tools. It evolved from the professional tool Easy-PC from NumberOne Software and is aimed at beginners and students.
The free software is full-featured for unlimited schematic designs and PCB layouts, with good libraries and tools to define custom components. It does, however, lack circuit simulation and 3D visualization. Connection to RS’ own parts library and PCB manufacture are optional. There’s also a Pro version to support large and complex projects, but unless you’re concerned about “blind and buried vias” or “hierarchical schematic design”, the free tool should be more than adequate.

– EAGLE (https://www.autodesk.com/products/eagle/)
Originally developed by CadSoft, EAGLE (Easily Applicable Graphical Layout Editor) was once one of the go-to free PCB design tools for hobbyists. Since its acquisition by Autodesk, free usage is now restricted only to hobbyists and students with a subsection to Fusion 360 for personal use. Confusingly, it overlaps significantly with Autodesk’s “Fusion Electronics”, which is built into Fusion 360. (See below.)
EAGLE has a reputation for ease of use, albeit a little old-fashioned, and good functionality. In addition to the usual schematic and layout features, it has capable auto-routing and 3D visualization. The restricted version limits designs to two schematic sheets, two signal layers, and a maximum board area of 80 cm2 (12.4 in2), all of which are enough for most simple projects.
Due largely to its heritage, there’s a large volume of tutorials and support materials available online, including many real-world examples from companies such as Adafruit and SparkFun. The tool also comes packaged with many starter projects. Support forums and groups are readily available and active.
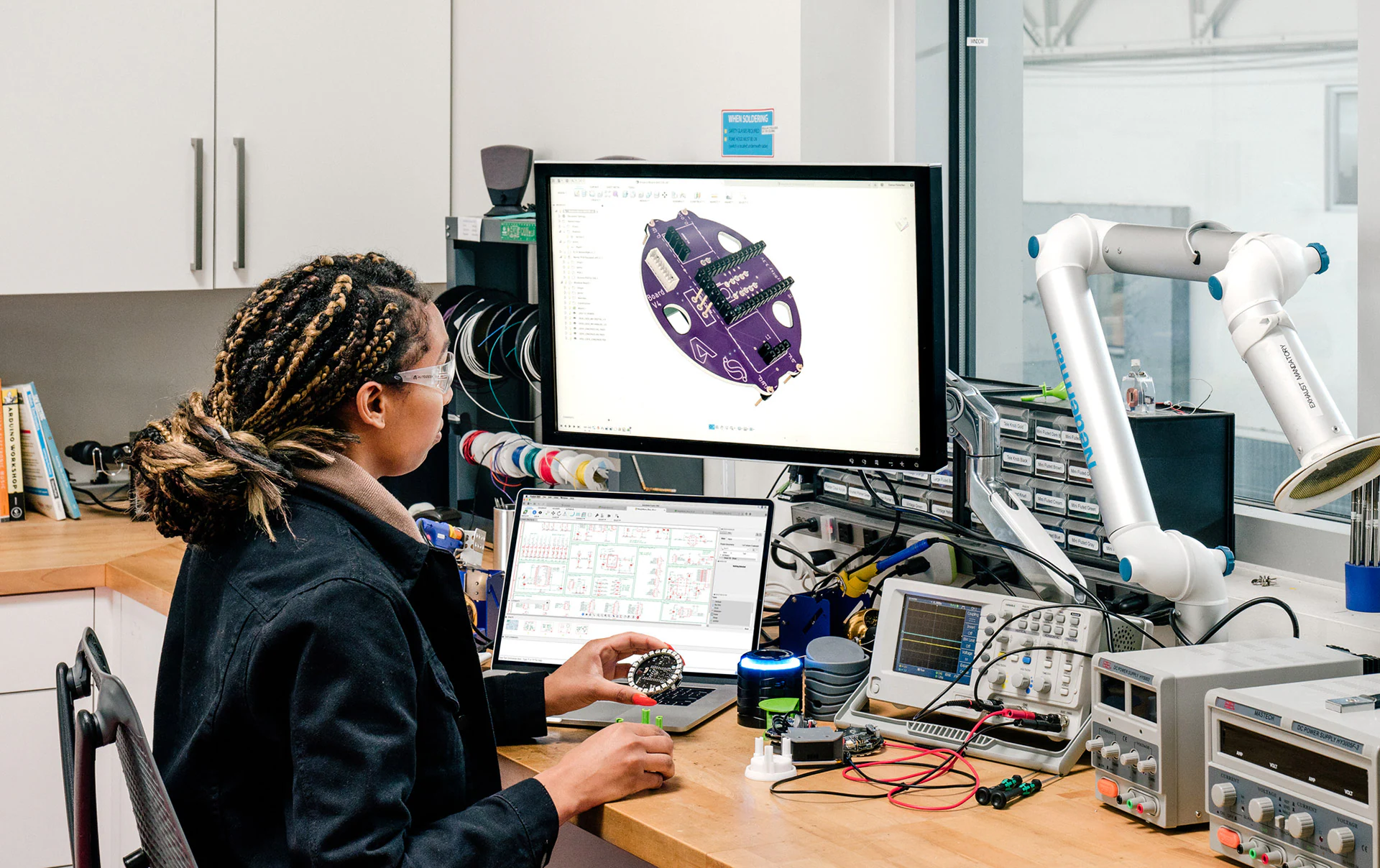

– Fusion Electronics ()
Fusion Electronics (sometimes called Fusion 360 Electronics) is Autodesk’s PCB and circuit design tool that’s directly integrated into its Fusion 360 CAD package.
Professional use incurs a license fee, but a restricted version is available with a subscription to Fusion 360 for personal use. Like EAGLE, one is limited to a maximum of two schematic sheets, two board layers, and a maximum board area of 80 cm2, but this should be adequate for most hobbyist use.
Initially criticized for being buggy and less functionally rich than EAGLE, Fusion Electronics appears to have caught up, although reports of slow updates continue. On the plus side, it shares the same UI as Fusion 360, offers multi-window design views, and is tightly integrated into Fusion 360’s 3D design operations in order to make housing design seamless.
Autodesk has committed to maintaining both EAGLE and Fusion Electronics as distinct products but have also been promoting training materials to help users move away from EAGLE, including a very comprehensive “Migration Guide“.

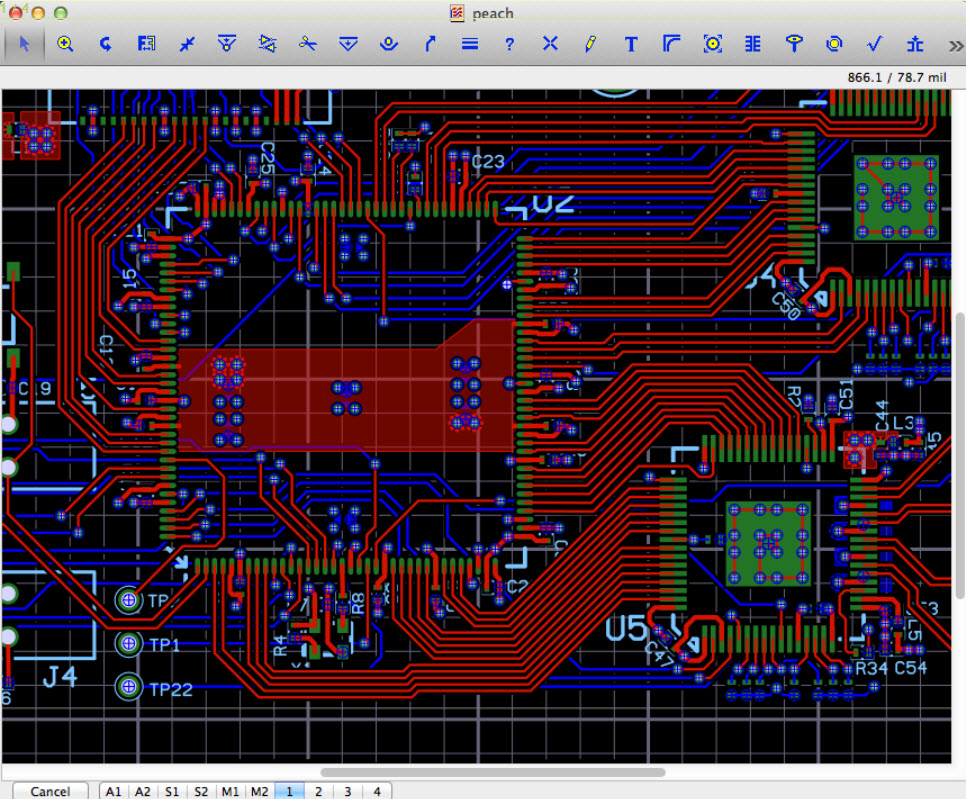
-Altium Designer (https://www.altium.com/altium-designer/)
As was already mentioned, Altium is one of the leading providers of EDA and PCB design solutions. Their premier design package, Altium Designer, is intended to provide an “uncompromising PCB design experience” for professionals. License fees are normally well over $1,000 per year, but students (with a valid university email address) can gain access for free for six months (on a renewable basis) during their studies.

-DipTrace (https://diptrace.com/diptrace-software/pcb-layout/)
DipTrace is schematic and PCB design software, by specialist provider Novarm, with a strong emphasis on ease of use without compromising functionality. The normal license fee is heavily discounted for not-for-profit and personal applications; students are allowed free use of the “Lite” version of the package with design limits of 500 pins and two board layers.
Augmenting the usual core functionality, DipTrace uses a very intuitive drag-and-drop approach optimized for 4K monitors (for those that have them), real-time 3D visualization, and simple design rule checking to help prevent errors, among other features.
ที่มา: https://all3dp.com/2/best-pcb-design-software/